
8 Models of Blended Learning
November 6, 2019Blended learning is one of the most common implementation strategies used consistently across all states. But the definition and usage models and examples vary widely (but not inaccurately) as the use of technology becomes a central point in our instruction.
I wouldn’t dare ask for a round-robin of sharing our ages. However, I will ask if you remember a time when technology wasn’t used in schools and classrooms – and even our homes? I’ll bravely date myself by saying that I remember when my family got their first computer! I also remember having to put tape over the phone so no one would use it while trying to connect to the internet. I also remember it taking fooorrrever to connect to the internet. And forget the hours it took to even download something!
If you can remember these nostalgic moments too, then you remember when technology in schools was scarce and highly coveted. And if you were in a school fortunate enough to start establishing their first computer lab you were even more appreciative.
Jump ahead to today.
Think about all the technology our students have access to now. And I’m not thinking about just in school. What about smartphones, e-readers, and the never-ending list of Apps that make learning, communicating, and connecting easier? Our kids (and us!) are completely plugged in, and for our students in our classrooms, they are digital natives. They don’t know what life was like before 3G or 4G. The point is that technology is deeply ingrained in our daily lives, both inside and outside of the classroom.
In fact, as soon as we started integrating online learning in schools, we became implementers of blended learning.
Blended learning isn’t so much a new idea or concept, but rather a natural evolution of the way we teach by leveraging technology, meeting the kids (our digital natives) where they are at today, and implementing various instructional models and strategies in the way we deliver our instruction that simultaneously leverages online learning.
The types of models based on the definition of blended learning is really where we launch this conversation.
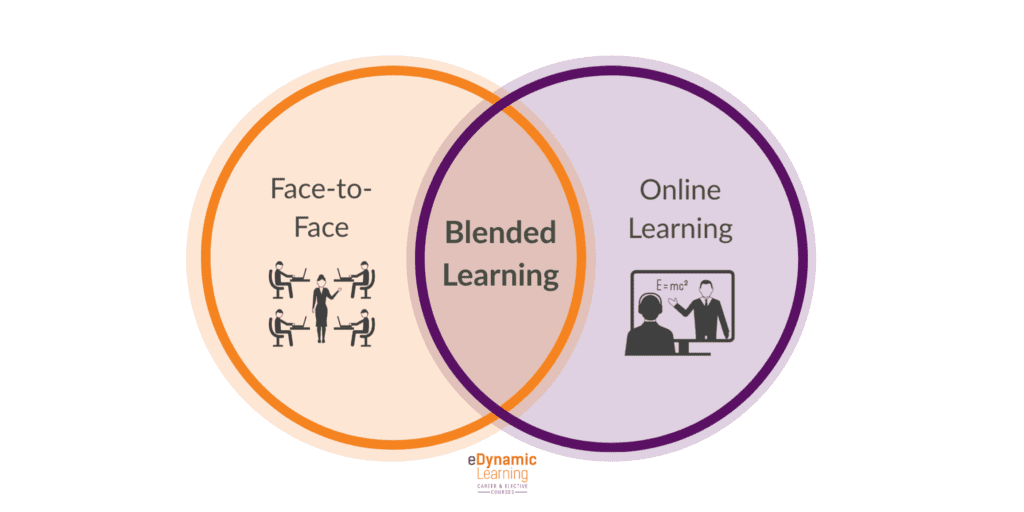
What is Blended Learning?
Honestly, I could ask teachers and administrators across the nation to define blended learning and there would be a lot of varying answers. Especially when we talk about the Flipped Classroom Model. But, at the core of all the different answers that might be provided, it’s safe to say that they will all be wrapped around the similar core nucleus of the merging of ‘traditional’ instruction and leveraging online technology. And they would be correct.
The ChristensonInstitute.org defines blended learning as having three parts:
- at least in part through online learning, with some element of student control over time, place, path, and/or pace;
- at least in part in a supervised brick-and-mortar location away from home;
- and the modalities along each student’s learning path within a course or subject are connected to provide an integrated learning experience.
With this definition in mind, blended learning supports and places emphasis on some elements of student-centered control in the form of time, pace, path, or place.
Common Blended Learning Models
Additionally, iNACOL adds that first the “traditional” instructional model must be changed up then the technology comes in acting as an “enabler to high-quality learning experiences” versus “driving” it, in order to support blended learning.
In any blended learning classroom, learning should be engaging and flexible to meet various needs. Additionally, online learning should be used in purposeful ways that support and drive bigger learning objectives.
Let’s discuss some common blended learning models found in classrooms and districts across the nation.
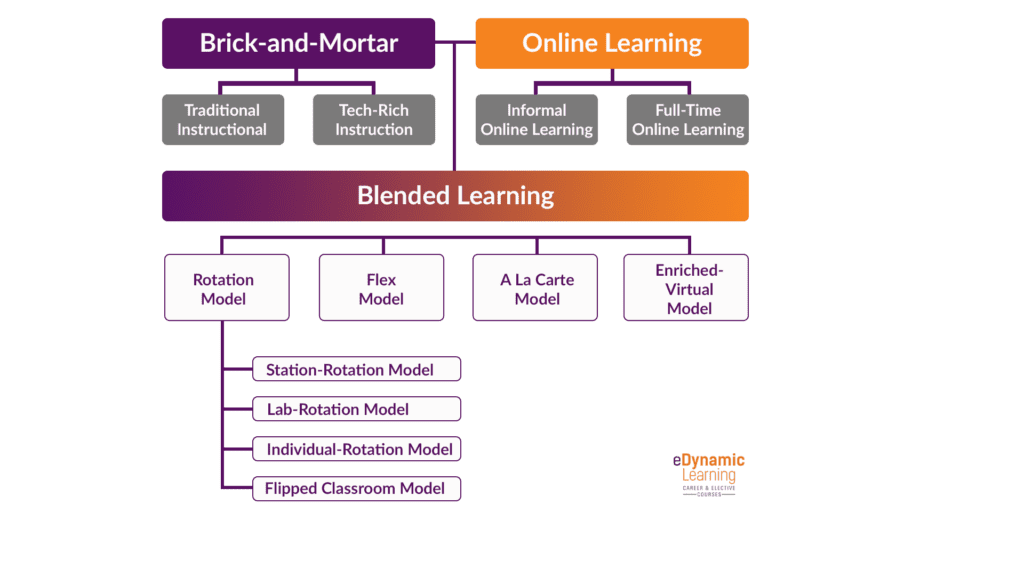
1. Station-Rotation Model
The most common model in many classrooms; especially in elementary. Students in this model rotate to different ‘stations’ during a fixed period of time. Stations are often referred to as ‘centers’ as well. One of these stations must allow for an activity that allows for online learning. For example, one year I was given 55-minute math blocks. As part of my station-rotation set-up, after my short direct instruction kick-off of the day, students then rotated through three different stations – one of which was leveraging online learning.
2. Lab-Rotation Model
This is another common model that schools with computer labs are familiar with and is similar to station-rotation. In this model, students rotate on a fixed schedule to a computer lab. We see this model in districts of all sizes. I’ve been in schools where the teacher uses “lab time” for students to initiate research and/or use various software (like Microsoft Office Suite, Google Suite, or Adobe Suite products) to complete assignments and projects. Additionally, I’ve worked in a school where the Instructional Technology Teacher, or Career and Technology Teacher partnered with the core classroom teacher to develop comprehensive project-based learning units.
3. Individual-Rotation Model
This is common in classrooms with a high focus on differentiation and personalization, including, but not limited to, Gifted and Talented programs and classes focusing on mastery. In this model, students work independently through assigned lessons or units of instruction, working towards mastery of understanding before ‘rotating’ to their next task on their own individual schedule. For example, in a G&T class I taught, each student had their own individualized playlist that they worked through. It included various activities, including instructional time with me, that they completed. This is a strong form of personalized learning in a blended learning model as it gives the student a high level of pace, place, voice, and choice.
4. Flipped Classroom Model
This is the most widely defined blended learning model, as many schools and classrooms adopt various forms of this strategy. In this model, students are introduced to content or concepts (typically through audio recordings or videos) outside the core classroom, including at home, then work through the practice and individual learning with the teacher and peers back in the core classroom. And this is where the name comes from because the learning structure is “flipped” in a traditional instructional model. Students are introduced to the new concept outside the classroom (what would typically be direct instruction), which allows for far more of the next day’s classroom time to be dedicated to practicing and applying the new concept with the teacher scaffolding support and working with peers towards a deeper understanding.
This model is quickly gaining traction in individual classrooms and across whole districts as more educators are finding the value and success with this instructional strategy. In fact, Clintondale High School in Clinton Township, Michigan, implemented the concept for its entire 400-student school almost a decade ago. When they first started out, they began with a single classroom of at-risk students and discovered that by the end of the school year, they were outperforming peers in other “traditional” classrooms.
eDynamic Learning’s embedded videos and highly popular unit audio podcasts are a great way to leverage eDL’s courses and lessons in a flipped classroom model. These all-inclusive audio summaries additionally support English language proficiency.
5. Project-Based Learning
This could be another topic to explore further in-depth. But, again, in the spirit of keeping it simple, project-based learning is where students learn through projects and is not to be confused with a culminating lesson or unit project. Rather, PBL is an opportunity for students to learn through projects. Think of PBL as learning through a unit of projects rather than a lesson. Essentially, this ‘hands-on, minds-on’ learning takes place over time. The integration of online learning is an essential component of PBL strategies and is often a perfect fit for STEAM classrooms.
eDynamic Learning’s Project-Based Learning guide supports teachers looking to establish project-based learning strategies in CTE and elective classrooms.
6. Remote (Virtual or Enriched Virtual) Model
As our students are faced with more and more challenges, such as having to work while in school or graduating on time with their cohort, many districts are turning towards the virtual or remote model of blended learning. In this model, students are not enrolled in a virtual school, but rather work on coursework remotely but still show up to their brick-and-mortar school for some face-to-face learning sessions. This typically places the student on a unique, ‘non-traditional’ schedule.
7. ‘Flex’ Learning Model
In this model, students work through online lessons at their own pace while in the brick-and-mortar classroom with the teacher available for support, guidance, and one-on-one instruction as well. This model truly gives students substantial flexibility and ownership over their learning.
8. A La Carte / Supplemental
Finding teachers for unique courses like Cybersecurity, Hospitality and Tourism, or Criminology may be challenging. For example, do you ever wish you could offer American Sign Language or Middle School Coding, but don’t have a teacher to provide instruction? The A La Carte model may be the solution you are looking for. This model allows students to take an online course with a ‘teacher of record’ then report to their ‘traditional’ classroom for other classes. The benefit allows students to take the courses they need when a teacher is unavailable for teaching the course, all while allowing the school to keep funds within the district.
eDynamic Learning offers instructional services that enable districts to offer a rich set of course options for students covering a broad range of topics. eDL can connect schools to highly-qualified, state-certified teachers in hard to find subject areas that offer virtual online teaching services. This allows districts to take advantage of easy onboarding and implementation at any time of the year and retain students and the associated FTE funding to expand the programs and staff they offer at their school.
In our next blended learning blog, we’ll be taking a look at various instructional strategies that can be used throughout the different models discussed here.
Get in Touch!
Are you ready to create blended learning classrooms at your school? eDynamic Learning not only provides schools with the largest library of career and technical education (CTE), elective, and Career Ready Program™ courses in the industry for grades 6-12, but also provides teachers with a Blended Learning Strategies guide (and Project-Based Learning guide) to use the courseware curriculum in flexible ways that take learning deeper and engage students in their future ahead. Get in touch with us today to learn more!
Check it Out!
Check out our on-demand webinar: Blended Learning with eDynamic Learning Courses
In this brief webinar, you’ll:
- get a high-level overview of some of the most popular blended learning implementation models
- learn how you can incorporate a blended learning model into your teaching strategies
- see how eDynamic Learning courses come to life and enable deeper learning through blended learning
——————
View All Blogs

